Tooth Extraction and Beyond: Your Guide to Essential Dental Procedures

Tooth Extraction and Beyond: Your Guide to Essential Dental Procedures
Estimated Reading Time: 8 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Tooth filling restores minor decay and prevents further damage.
- Tooth extraction removes irreparable teeth; see our guide.
- Severe decay, infection, or crowding may lead to extraction (Source).
- Early gingivitis is reversible with professional and home care.
- Advanced periodontitis requires deep cleaning or surgery.
- Receding gums treatments manage sensitivity and restore tissue.
Table of Contents
Tooth Filling
Definition & Indications: A filling repairs and restores a tooth affected by decay. Ideal for early-stage decay or small cavities.
Materials Overview:
- Composite resin: Natural color for front teeth.
- Amalgam: Durable for back teeth.
- Ceramic: High aesthetics at a higher cost.
Step-by-Step Procedure:
- Local anesthetic application.
- Decay removal with dental tools.
- Cavity cleaning and disinfection.
- Filling placement, shaping, and curing.
- Polishing for smooth finish.
Lifespan & Maintenance: Lasts 5–15 years depending on material and hygiene practices. Regular brushing, flossing, and check-ups are essential.
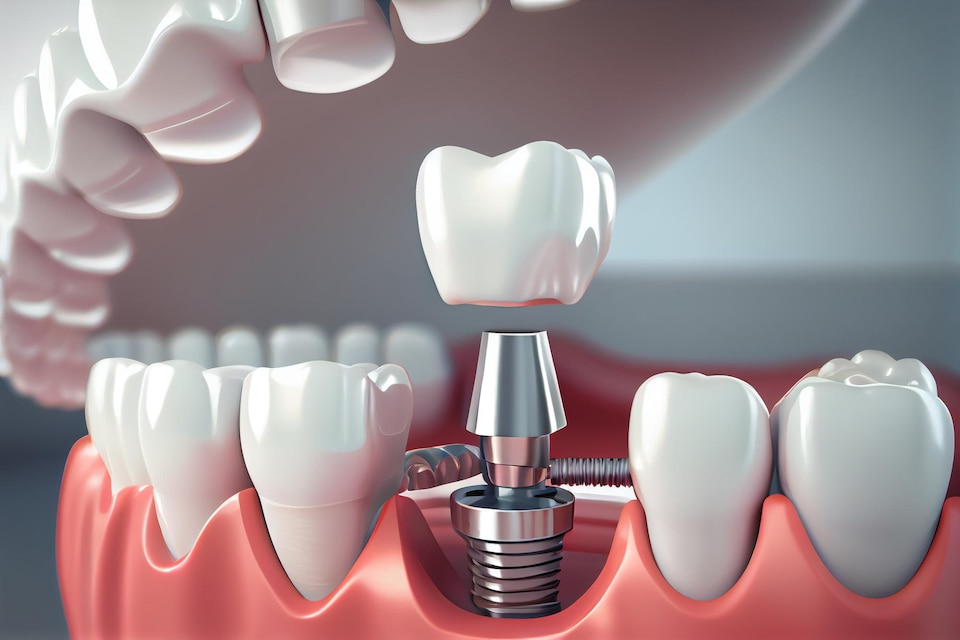
Tooth Extraction
Definition & Clinical Indications: Extraction removes a tooth when decay, infection, or crowding makes it irreparable. Source
Extraction Types:
- Simple extraction: Removal of a visible tooth using elevators and forceps.
- Surgical extraction: For impacted or broken teeth, involving gum incision. Source
Detailed Procedure:
- Local anesthesia to numb the area.
- Tooth loosening and removal.
- Site cleaning and suturing if needed.
Post-Extraction Care: Bite on gauze to control bleeding, avoid spitting or straws, stick to soft foods, resume normal hygiene after 24 hours.
Cost & Financing: Varies by complexity; most insurance plans cover some costs.
Gingivitis Treatment
Definition & Warning Signs: Inflammation, redness, and bleeding of the gums, reversible with proper care.
Professional Approaches: Routine cleanings and antimicrobial rinses.
Home Care: Brush twice daily with a soft brush, floss regularly, and use an ADA-approved mouthwash.
Gum Disease Treatment
Disease Progression: Untreated gingivitis can advance to periodontitis, leading to bone loss and tooth loss.
Non-Surgical Procedures: Scaling and root planing remove plaque and tartar below the gumline.
Surgical Interventions: Flap surgery and bone grafts for advanced cases.
Maintenance & Follow-Up: Regular visits to monitor gum health and prevent recurrence.
Receding Gums Treatment
Causes & Consequences: Caused by aggressive brushing or genetics, resulting in sensitivity and cavity risk on exposed roots.
Non-Surgical Management: Desensitizing agents and gentle brushing techniques.
Surgical/Graft Procedures: Tissue grafts to cover exposed roots.
FAQ
- What is tooth extraction?
- Tooth extraction is the process of removing a tooth that cannot be saved by other treatments.
- How should I care for my mouth after extraction?
- Bite on gauze, avoid rinsing vigorously, and stick to soft foods for the first 24 hours.
- What is the difference between gingivitis and periodontitis?
- Gingivitis affects only the gums and is reversible; periodontitis affects bone and can cause tooth loss.
For more resources, visit our homepage here. Book your appointment today here.